FAQS
Unlocking Industrial Efficiency: The Science Behind Infrared Heating Technology
In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, maximizing efficiency is paramount for competitive advantage. One of the most promising technologies to achieve this goal is the utilization of industrial infrared heaters. These innovative heating solutions utilize the principles of infrared radiation to provide targeted, energy-efficient heat, significantly reducing energy consumption and enhancing operational productivity.
Unlike traditional heating methods that warm the air, industrial infrared heaters directly heat objects and materials, ensuring faster processing times and more uniform temperature distribution. This article explores the science behind infrared heating technology, emphasizing its potential to unlock new levels of efficiency within various industrial applications. With advancements in digital control and monitoring systems, industries can now harness the full capabilities of industrial infrared heaters, leading to optimized processes and substantial cost savings.
Understanding Infrared Heating Technology: Principles and Mechanisms
Infrared heating technology operates on the principles of radiation, fundamentally distinguishing itself from traditional heating methods such as convection. In infrared heating, electromagnetic waves are emitted, which directly transfer heat to objects and surfaces without heating the surrounding air significantly. This efficiency stems from the ability of infrared waves to penetrate materials and excite their molecules, leading to rapid temperature increases. As a result, industrial applications can realize substantial energy savings while enhancing operational efficiency.
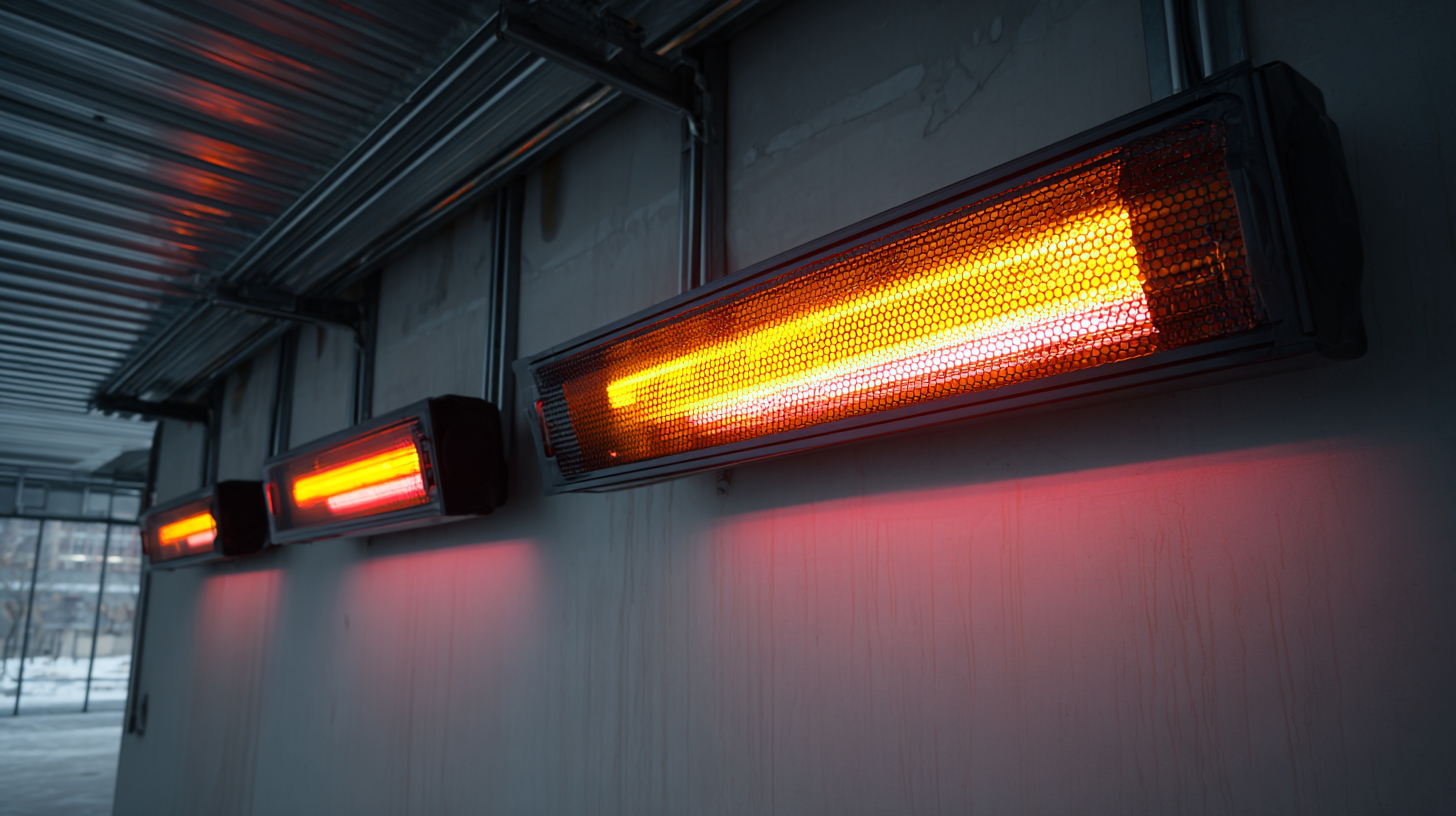

The mechanisms behind infrared heating involve the interaction of infrared radiation with different surfaces. Materials such as metals and ceramics absorb infrared radiation effectively, converting it into thermal energy. This selective absorption enables precise temperature control, making infrared heating ideal for applications such as curing paints, drying coatings, and even in food processing. By understanding these principles and mechanisms, industries can leverage infrared technology to optimize production processes, reduce heating time, and minimize energy consumption, all while maintaining the quality and integrity of the materials involved.
The Role of Infrared Heating in Boosting Industrial Energy Efficiency
Infrared heating is revolutionizing industrial energy efficiency through its unique ability to directly heat materials without warming the surrounding air. According to a report by the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE), infrared heating systems can achieve efficiencies of up to 90%, significantly outperforming traditional convection-based heating methods. This efficiency results from the way infrared rays penetrate directly into objects, enabling faster heat-up times and reduced energy consumption. With energy costs rising, industries are increasingly turning to infrared technology to optimize their heating processes and reduce operational expenses.
Additionally, sectors such as manufacturing and food processing have reported substantial energy savings by integrating infrared heating into their operations. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that industries implementing infrared heating technology experienced an average energy reduction of 30-50%, translating into operational savings of up to $250,000 annually for large facilities. This trend underscores the importance of embracing advanced heating technologies to enhance productivity while achieving environmental sustainability goals. Adopting infrared heating not only streamlines processes but also contributes to a significant decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Unlocking Industrial Efficiency: The Impact of Infrared Heating Technology
This chart illustrates the advantages of infrared heating technology compared to conventional heating methods. Key metrics such as energy consumption, production output, heating speed, and cost savings are compared to highlight the enhancements in industrial energy efficiency achieved through infrared heating.
Comparative Analysis: Infrared Heating vs. Conventional Heating Methods
Infrared heating technology has emerged as a powerful alternative to conventional heating methods, offering distinct advantages in efficiency and effectiveness. Unlike traditional systems that heat the air, infrared heaters work by emitting radiant energy that directly warms objects and surfaces in its path. This approach minimizes heat loss and enhances comfort, making it a highly efficient choice for both industrial and residential applications.
When comparing infrared heating to conventional methods such as steam or forced air heating, the differences become evident. Conventional systems often require significant time to warm up and can result in uneven heat distribution. In contrast, infrared heating provides immediate warmth and more uniform temperature across the targeted area. Furthermore, infrared heaters generally consume less energy, leading to reduced operational costs and a smaller environmental footprint. This comparative analysis underscores the growing appeal of infrared technology in achieving industrial efficiency.
Applications of Infrared Heating Across Various Industries and Their Impact
Infrared heating technology is revolutionizing industries by providing efficient and targeted heating solutions. This technology finds applications across various sectors, from manufacturing and food processing to healthcare and construction. According to a report by Grand View Research, the infrared heating market is projected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions. In manufacturing, infrared heating enables faster production cycles, reducing energy consumption by up to 50% compared to conventional heating methods. This not only translates to cost savings but also minimizes environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In the food processing industry, infrared heating is utilized for drying, cooking, and sterilization processes, significantly enhancing efficiency. The Food Processing Technology Report highlights that infrared cooking can reduce cooking times by nearly 30%, leading to higher throughput and better product quality. Additionally, in the healthcare sector, infrared heating is used in physiotherapy and rehabilitation, aiding in pain relief and accelerating recovery times. The versatility of infrared technology makes it a vital tool in enhancing operational efficiency and productivity while catering to the specific needs of diverse industries.
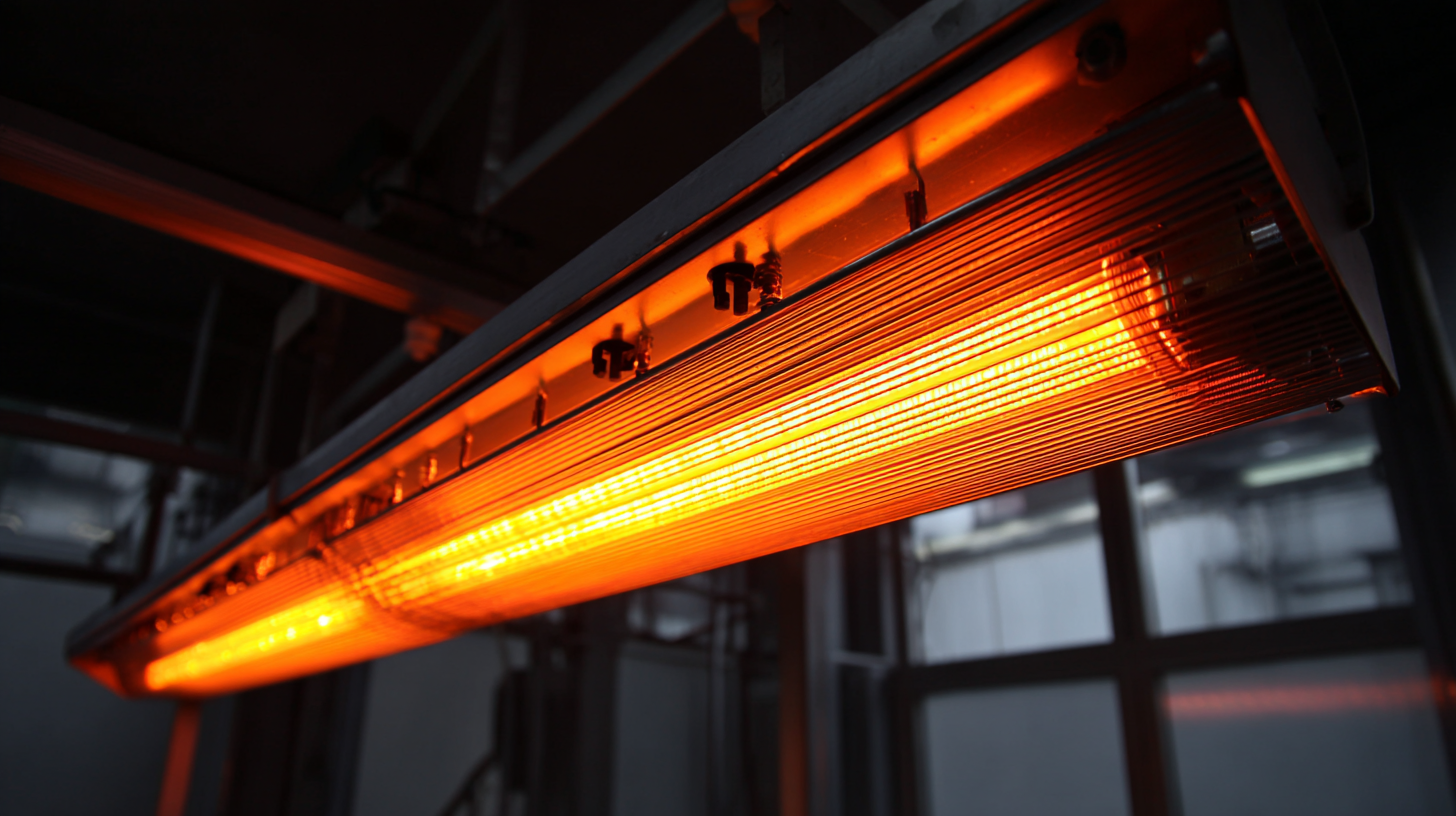

Quantifying the Benefits: Cost Savings and Reduced Carbon Footprint with Infrared Solutions
Infrared heating technology represents a pivotal shift in industrial heating solutions, particularly in terms of cost efficiency and environmental responsibility. By directly warming objects rather than the air around them, infrared heaters enable rapid temperature increases and reduced energy consumption. This targeted approach not only minimizes energy wastage but also significantly lowers operational costs, making it a financially viable option for many businesses.
Moreover, adopting infrared heating has a positive impact on carbon footprints. Traditional heating methods often rely on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, infrared solutions can use renewable energy sources, further enhancing their sustainability credentials. Many companies report a measurable reduction in their carbon emissions after switching to infrared technology, aligning their operations with global efforts to combat climate change while also satisfying increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. As industries seek to improve their sustainability practices, the quantifiable benefits of infrared heating technology become increasingly attractive.
Unlocking Industrial Efficiency: The Science Behind Infrared Heating Technology
| Parameter | Conventional Heating | Infrared Heating | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency (%) | 60-70 | 85-95 | +25% |
| Average Cost per kWh ($) | 0.10 | 0.08 | -0.02 |
| Carbon Emissions (kg CO2/kWh) | 0.5 | 0.3 | -0.2 |
| Installation Time (hours) | 40 | 30 | -10 |
| Maintenance Frequency (annual) | 2 | 1 | -1 |
Related Posts
-

How Infrared Bar Heaters Work: The Science Behind Efficient Heating Solutions
-

Portable Heaters Innovation Trends Unveiled at 2025 Canton Fair China 138th Session
-

Discover the Best Outdoor Heaters in the UK to Transform Your Winter Evenings
-

Unlocking Warehouse Heaters Market Trends at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

How to Choose the Right Commercial Electric Heaters for Your Business Needs
-

Exploring Innovations in Gas Patio Heater Products at the 2025 Canton Fair
 Skip to content
Skip to content
